March 4 stands as one of history’s most eventful days, witnessing the rise and fall of empires, groundbreaking discoveries, and moments that shaped our modern world across centuries of human achievement.

Politics and Government Events on March 4
1901 – William McKinley Inaugurated for Second Presidential Term
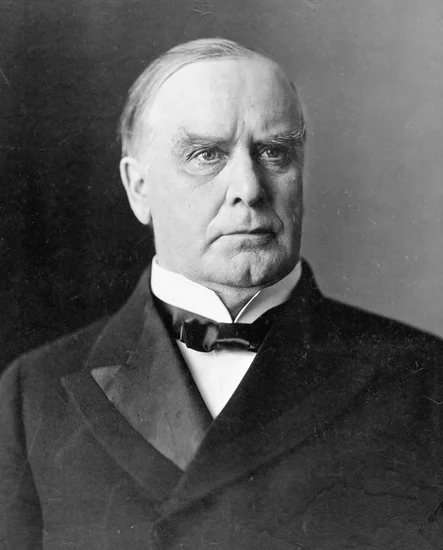

President William McKinley took the oath of office for his second term with Theodore Roosevelt as his new vice president. The ceremony marked the beginning of what would become a pivotal period in American politics.
Roosevelt’s elevation to the vice presidency positioned him perfectly for his eventual ascension to the presidency. McKinley’s second inaugural would tragically become his final major political milestone.
1933 – Franklin D. Roosevelt Becomes 32nd President

Franklin Delano Roosevelt assumed the presidency during America’s darkest economic hour, inheriting a nation gripped by the Great Depression. His inaugural address promised bold action to restore national confidence.
Roosevelt’s famous declaration that “the only thing we have to fear is fear itself” resonated across the country. His presidency would fundamentally transform the relationship between federal government and American citizens.
1933 – Austrian Parliament Suspended Under Dollfuss
Chancellor Engelbert Dollfuss exploited a procedural dispute to suspend Austria’s Parliament and establish authoritarian rule by decree. This constitutional crisis marked Austria’s decisive turn away from democratic governance.
The suspension eliminated parliamentary opposition to Dollfuss’s increasingly dictatorial policies. Austria’s democratic institutions would not recover until after World War II.
1913 – United States Department of Labor Established
Congress created the Department of Labor as a cabinet-level agency to protect and advance American workers’ interests. The new department consolidated various federal labor functions under unified leadership.
This landmark legislation reflected growing recognition of labor issues in industrial America. The department would play crucial roles in workplace safety, wage standards, and labor relations.
1917 – Jeannette Rankin Enters Congress

Jeannette Rankin of Montana became the first woman to serve in the United States House of Representatives. Her historic election shattered the all-male composition of Congress.
Rankin’s groundbreaking achievement came four years before women gained universal suffrage. Her presence in Congress symbolized the advancing women’s rights movement across America.
1980 – Robert Mugabe Wins Zimbabwe Elections
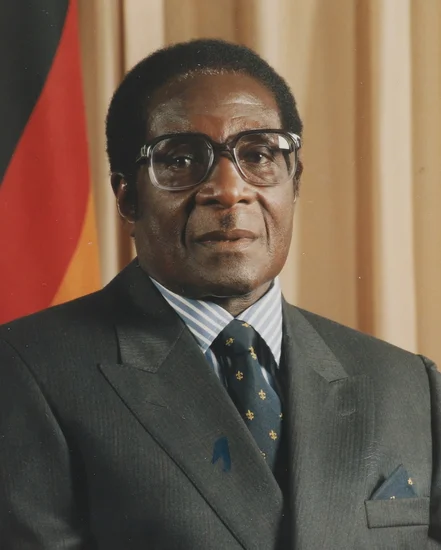

Nationalist leader Robert Mugabe secured a decisive electoral victory to become Zimbabwe’s first black prime minister. His triumph marked the end of white minority rule in the former Rhodesia.
Mugabe’s election victory fulfilled promises of black majority rule after years of guerrilla warfare. The results transformed Zimbabwe’s political landscape and concluded its liberation struggle.
2009 – International Criminal Court Issues Arrest Warrant
The International Criminal Court issued an unprecedented arrest warrant for sitting Sudanese President Omar Hassan al-Bashir. The charges included war crimes and crimes against humanity in Darfur.
Al-Bashir became the first serving head of state indicted by the ICC since its establishment. The warrant sparked international diplomatic tensions and debates about sovereignty versus justice.
Military and Naval History on March 4
1941 – Operation Claymore Launched on Lofoten Islands
British forces executed Operation Claymore, the first large-scale commando raid of World War II, targeting German positions in Norway’s Lofoten Islands. The daring assault demonstrated Britain’s commitment to offensive operations.
The raid successfully destroyed German infrastructure and captured valuable intelligence materials. Operation Claymore boosted British morale and established the template for future commando operations.
1943 – Battle of the Bismarck Sea Concludes
The Battle of the Bismarck Sea reached its devastating conclusion as Allied forces annihilated a Japanese convoy attempting to reinforce New Guinea. The victory eliminated crucial Japanese reinforcements and supplies.
Allied air power proved decisive in this engagement, demonstrating the effectiveness of coordinated bombing attacks. The battle severely weakened Japanese capabilities in the Southwest Pacific theater.
1944 – USAAF Begins Daylight Bombing of Berlin
Following the success of Big Week operations, the United States Army Air Forces launched sustained daylight bombing campaigns against Nazi Germany’s capital. These raids brought the war directly to the heart of the Third Reich.
The bombing campaign marked a strategic shift toward targeting Germany’s political and administrative centers. Berlin’s civilians experienced the full horror of total war as Allied bombers appeared overhead.
1913 – Greek Victory at Bizani
Greek forces engaged Turkish troops at Bizani during the First Balkan War, achieving victory two days later. This battle contributed to the Ottoman Empire’s declining influence in southeastern Europe.
The Greek triumph at Bizani demonstrated the effectiveness of Balkan League coordination against Ottoman forces. The victory advanced Greek territorial ambitions and weakened Turkish defensive positions.
2002 – Operation Anaconda Casualties in Afghanistan
Seven American Special Operations Forces soldiers died alongside 200 Al-Qaeda fighters during reconnaissance missions in Afghanistan’s Shah-i-Kot Valley. The casualties highlighted the dangerous nature of counter-terrorism operations.
The engagement demonstrated Al-Qaeda’s continued resistance capabilities despite previous military defeats. American forces faced determined opposition in Afghanistan’s challenging mountain terrain.
Science and Discovery Milestones on March 4
1986 – Soviet Vega 1 Images Halley’s Comet
The Soviet Vega 1 spacecraft began transmitting unprecedented images of Halley’s Comet, including the first detailed photographs of its nucleus. These images revolutionized scientific understanding of cometary composition.
The spacecraft’s successful flyby provided invaluable data about comet structure and behavior. Soviet space technology achieved a remarkable milestone in deep space exploration and planetary science.
1925 – FDA Approves HIV Blood Test
The Food and Drug Administration approved the first blood test for HIV infection, fundamentally transforming blood donation safety protocols. This breakthrough protected America’s blood supply from contamination.
The test’s implementation marked a crucial victory in the fight against AIDS transmission. Medical professionals gained essential tools for protecting patients requiring blood transfusions.
1955 – Saimaa Ringed Seal Protection Order
Finland enacted legal protection for the endangered Saimaa ringed seal, one of the world’s rarest marine mammals. This conservation measure addressed the species’ critically low population numbers.
The protection order represented early recognition of human responsibility for endangered species preservation. Finland’s action established important precedents for marine mammal conservation efforts.
1962 – Caledonian Airways DC-7 Crash Investigation
A Caledonian Airways Douglas DC-7 crashed shortly after takeoff from Cameroon, killing all 111 people aboard in the aircraft type’s worst accident. The disaster prompted comprehensive safety investigations.
Aviation authorities examined mechanical failures and operational procedures following the tragedy. The crash contributed to improved safety standards for commercial aviation worldwide.
Cultural and Arts Events on March 4
1966 – John Lennon’s “More Popular Than Jesus” Interview
Beatles member John Lennon declared in a London Evening Standard interview that his band had become “more popular than Jesus now.” The controversial statement sparked international religious and cultural debates.
Lennon’s comments reflected the Beatles’ unprecedented global influence and cultural impact. The controversy highlighted tensions between popular culture and traditional religious values.
1916 – Franz Marc Dies at Verdun

German Expressionist painter Franz Marc died in the Battle of Verdun, cutting short one of Europe’s most promising artistic careers. His death symbolized the devastating impact of World War I on cultural development.
Marc’s vibrant animal paintings and contributions to Der Blaue Reiter movement influenced modern art’s evolution. The war’s brutality eliminated countless creative talents across Europe.
1963 – William Carlos Williams Passes Away

American poet William Carlos Williams died, concluding a career that revolutionized modern poetry through his imagist techniques and everyday language. His work influenced generations of American writers.
Williams championed American vernacular and local subjects over European literary traditions. His innovative approach to poetry established distinctly American artistic voices.
1994 – John Candy Dies Unexpectedly

Beloved Canadian comedian and actor John Candy died suddenly, shocking fans worldwide who cherished his performances in countless comedy films. His death marked the end of an era in popular comedy.
Candy’s warmth and humor brought joy to millions through his memorable film roles. His unexpected passing left a significant void in entertainment and comedy.
Religious and Social Events on March 4
1933 – Frances Perkins Becomes First Female Cabinet Member
The United States Senate confirmed Frances Perkins as Secretary of Labor, making her the first woman to serve in a presidential cabinet. Her appointment broke significant gender barriers in American government.
Perkins would serve throughout Roosevelt’s presidency, championing workers’ rights and social security programs. Her tenure established important precedents for women in high-level government positions.
1944 – Fannie Barrier Williams Dies

Pioneering African American educator and activist Fannie Barrier Williams died, concluding a lifetime dedicated to advancing civil rights and women’s education. Her work bridged racial and gender equality movements.
Williams challenged discrimination through her involvement in women’s clubs and educational institutions. Her legacy inspired future generations of civil rights activists.
1977 – Vrancea Earthquake Devastates Romania

A powerful earthquake struck eastern and southern Europe, killing more than 1,500 people, primarily in Bucharest, Romania. The disaster highlighted the region’s seismic vulnerabilities and emergency preparedness needs.
The earthquake’s destruction prompted international humanitarian assistance and improved building codes. Romania’s recovery efforts demonstrated community resilience in the face of natural disasters.
1918 – Spanish Flu Pandemic Begins
The first recorded case of influenza appeared at Camp Funston, Kansas, marking the conventional beginning of the worldwide Spanish flu pandemic. This outbreak would become one of history’s deadliest pandemics.
The pandemic would ultimately kill millions worldwide, demonstrating the global interconnectedness of public health threats. Military camps accelerated the disease’s rapid spread across continents.
Business and Economic Events on March 4
1957 – S&P 500 Stock Index Introduced
Standard & Poor’s launched the S&P 500 stock market index, replacing the previous S&P 90 and establishing what would become America’s premier market benchmark. The expanded index provided broader market representation.
The S&P 500’s introduction revolutionized investment analysis and portfolio management strategies. Financial professionals gained a more comprehensive tool for measuring market performance.
1909 – Saxbe Fix Employed for Knox Appointment

President William Taft used the Saxbe fix mechanism to circumvent constitutional restrictions and appoint Philander C. Knox as Secretary of State. This legal maneuver addressed conflicts between congressional service and executive appointments.
The Saxbe fix became an important precedent for resolving constitutional appointment conflicts. Taft’s innovative approach demonstrated creative solutions to governmental structural problems.
1960 – French Freighter Explodes in Havana
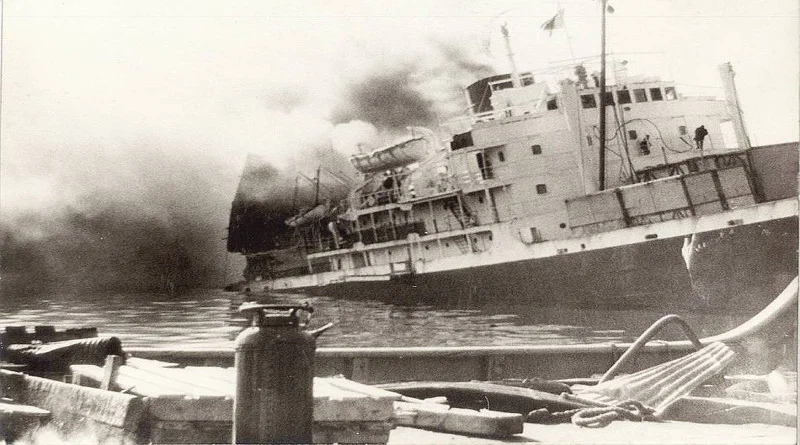

The French freighter La Coubre exploded in Havana harbor, killing 100 people and raising suspicions of sabotage during Cuba’s revolutionary period. The disaster occurred amid heightening Cold War tensions.
The explosion’s cause remained disputed, with various parties blamed for the tragedy. The incident contributed to deteriorating relations between Cuba and Western nations.
1996 – Weyauwega Train Derailment
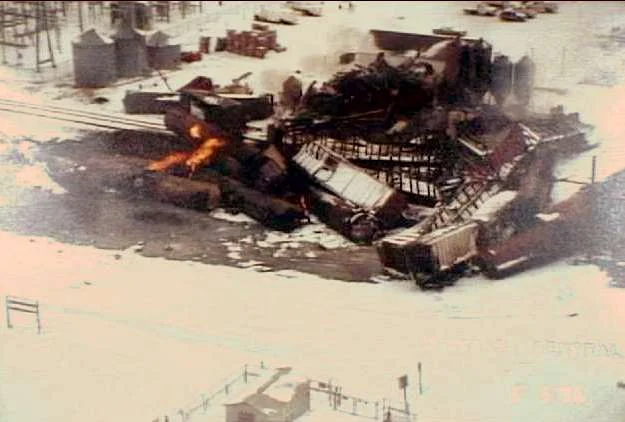

A derailed train in Weyauwega, Wisconsin, forced the emergency evacuation of 2,300 residents for 16 days due to hazardous material concerns. The incident highlighted risks associated with transporting dangerous chemicals.
The extended evacuation demonstrated the serious public safety implications of railway accidents. Communities learned important lessons about emergency preparedness and industrial transportation safety.
Transportation and Infrastructure on March 4
1994 – Space Shuttle Columbia Launches STS-62
Space Shuttle Columbia launched on mission STS-62, continuing America’s space exploration program and conducting crucial scientific experiments in microgravity. The mission advanced understanding of materials science and biological processes.
Columbia’s successful launch demonstrated the Space Shuttle program’s ongoing contributions to scientific research. The mission’s experiments provided valuable data for future space exploration initiatives.
1966 – Canadian Pacific Airlines Crash at Tokyo
A Canadian Pacific Air Lines DC-8-43 exploded during landing at Tokyo International Airport, killing 64 people and highlighting international aviation safety concerns. The tragedy prompted enhanced airport security measures.
The explosion’s investigation revealed important safety deficiencies in international aviation protocols. Airlines implemented improved safety procedures following the comprehensive accident analysis.
1970 – French Submarine Eurydice Disaster
The French submarine Eurydice exploded underwater, resulting in the complete loss of its 57-man crew and shocking the French Navy. The disaster highlighted inherent dangers in submarine operations.
The tragedy prompted comprehensive reviews of submarine safety procedures and emergency protocols. Naval authorities implemented enhanced safety measures to prevent similar disasters.
2018 – Nik Wallenda Walks Over Masaya Volcano

Daredevil Nik Wallenda became the first person to walk across Nicaragua’s active Masaya Volcano, demonstrating extraordinary courage and skill. His achievement captivated audiences worldwide and pushed the boundaries of human endurance.
Wallenda’s volcanic walk required extensive preparation and specialized equipment to survive the extreme conditions. The feat represented a remarkable combination of athletic ability and technological innovation.
Sports and Recreation on March 4
1990 – Hank Gathers Collapses During Game

Loyola Marymount basketball star Hank Gathers died after collapsing during a West Coast Conference tournament semifinal game. His sudden death shocked the basketball world and highlighted cardiac health issues in athletics.
Gathers’ death prompted increased awareness of heart conditions in young athletes. His team’s subsequent NCAA tournament run became one of sports’ most emotional stories.
2022 – Rod Marsh Dies
Australian cricket legend Rod Marsh died, concluding a career that established him as one of the sport’s greatest wicket-keepers. His death marked the end of an era in Australian cricket.
Marsh’s contributions to cricket extended beyond his playing career through coaching and administration. His influence shaped generations of Australian cricketers and international cricket development.
2022 – Shane Warne Passes Away

Australian cricket icon Shane Warne died unexpectedly, shocking the cricket world and millions of fans globally. His death eliminated one of cricket’s most charismatic and skilled players.
Warne revolutionized spin bowling and became cricket’s most celebrated leg-spinner. His personality and playing style transcended cricket, making him a global sporting icon.
Notable Births on March 4
1904 – George Gamow Born

Ukrainian-American physicist George Gamow entered the world, destined to become one of the most influential cosmologists of the 20th century. His childhood curiosity about the universe shaped his future scientific pursuits.
Gamow would later develop groundbreaking theories about the Big Bang and stellar nucleosynthesis. His work fundamentally advanced understanding of cosmic evolution and nuclear physics.
1932 – Miriam Makeba Born

South African singer Miriam Makeba was born, later becoming known worldwide as “Mama Africa” for her powerful voice and anti-apartheid activism. Her musical talents emerged early in her childhood.
Makeba’s international career brought global attention to South African music and apartheid’s injustices. Her artistic achievements combined entertainment with powerful social commentary.
1947 – Kenny Dalglish Born

Scottish footballer Kenny Dalglish was born, destined to become one of soccer’s greatest players and managers. His early years in Glasgow shaped his lifelong passion for the beautiful game.
Dalglish achieved legendary status at Celtic and Liverpool, winning numerous championships as both player and manager. His tactical intelligence and leadership qualities distinguished him throughout his career.
1965 – Khaled Hosseini Born

Afghan-American novelist Khaled Hosseini was born, later becoming one of the most acclaimed contemporary writers. His multicultural background would profoundly influence his literary works.
Hosseini’s novels, including “The Kite Runner,” brought Afghan culture and history to global audiences. His storytelling bridged cultural divides and promoted understanding across different societies.
1967 – Landon Donovan Born

American soccer player Landon Donovan was born, destined to become the face of American soccer and its greatest international player. His athletic abilities manifested early in his California childhood.
Donovan’s career elevated American soccer’s profile and inspired a generation of young players. His World Cup performances and Major League Soccer success established him as an American sporting icon.
1927 – Patrick Moore Born
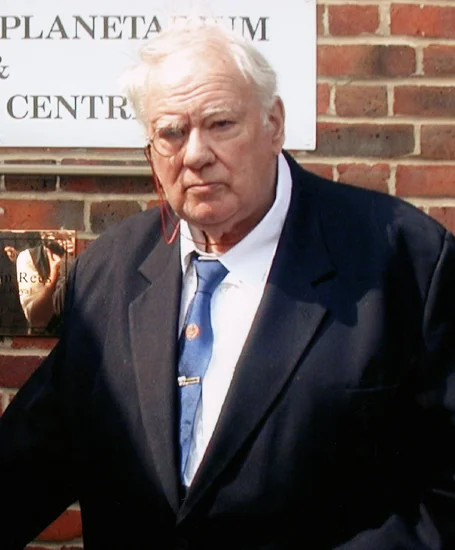

English astronomer Patrick Moore was born, later becoming Britain’s most beloved popularizer of astronomy through his television programs. His lifelong fascination with the stars began in childhood.
Moore’s “The Sky at Night” program ran for over 50 years, inspiring countless people to explore astronomy. His enthusiasm and knowledge made complex astronomical concepts accessible to general audiences.
1948 – James Ellroy Born

American crime novelist James Ellroy was born, later becoming one of the most distinctive voices in contemporary literature. His troubled childhood would profoundly influence his dark, complex novels.
Ellroy’s works, including “L.A. Confidential,” redefined crime fiction through their innovative narrative techniques. His exploration of American corruption and violence established him as a literary master.
1958 – Patricia Heaton Born

American actress Patricia Heaton was born, later achieving fame through her television performances and comedic talents. Her midwestern upbringing shaped her relatable, down-to-earth persona.
Heaton’s roles in “Everybody Loves Raymond” and “The Middle” made her one of television’s most beloved performers. Her comedic timing and authentic portrayals resonated with millions of viewers.
Notable Deaths on March 4
1925 – James Ward Dies
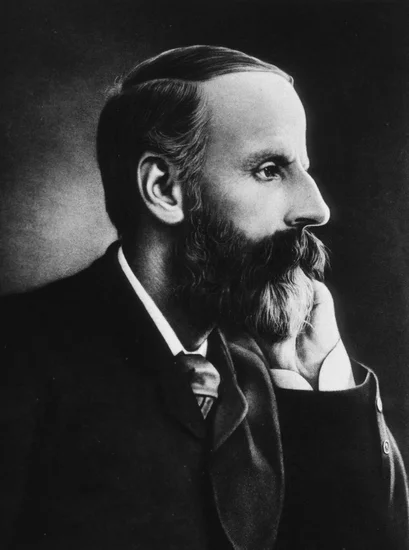

English psychologist and philosopher James Ward died, concluding a career that significantly advanced understanding of consciousness and perception. His work influenced generations of psychological theorists.
Ward’s contributions to psychology bridged philosophical inquiry with empirical research. His theories about mental processes laid important groundwork for modern psychological science.
1940 – Hamlin Garland Dies

American novelist and short story writer Hamlin Garland died, ending a literary career that captured the American frontier experience. His realistic portrayals of rural life earned critical acclaim.
Garland’s works documented the challenges and hardships of agricultural communities in the late 19th century. His writing provided valuable insights into American social and economic transformation.
1952 – Charles Scott Sherrington Dies
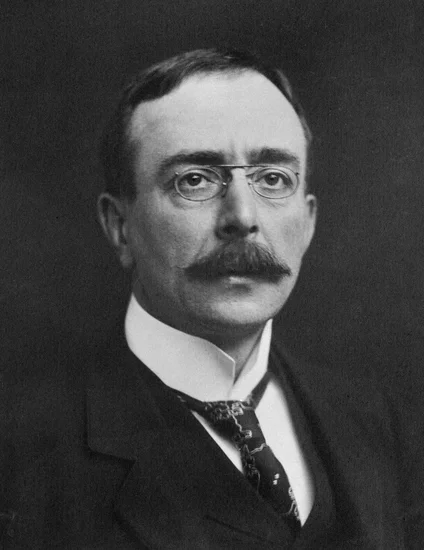

English neurophysiologist Charles Scott Sherrington died, concluding a career that earned him the Nobel Prize and fundamentally advanced neuroscience. His research revolutionized understanding of nervous system function.
Sherrington’s work on reflexes and neural integration established foundational principles of modern neuroscience. His discoveries about synaptic transmission influenced medical practice and scientific research.
1999 – Harry Blackmun Dies

American Supreme Court Justice Harry Blackmun died, ending a judicial career that included authoring the landmark Roe v. Wade decision. His legal philosophy evolved significantly during his tenure.
Blackmun’s transformation from conservative to liberal justice reflected his deep engagement with constitutional interpretation. His opinions addressed crucial issues of individual rights and social justice.
2008 – Gary Gygax Dies

American game designer Gary Gygax died, concluding a career that revolutionized gaming through his co-creation of Dungeons & Dragons. His imagination transformed entertainment and popular culture.
Gygax’s innovative game design established the foundation for modern role-playing games and fantasy gaming. His creativity influenced countless gamers and contributed to the development of digital entertainment.
2019 – Luke Perry Dies

American actor Luke Perry died unexpectedly, shocking fans who remembered him from “Beverly Hills, 90210” and “Riverdale.” His death highlighted the fragility of life and the impact of sudden loss.
Perry’s performances defined teenage television drama for a generation of viewers. His unexpected passing reminded audiences of the personal connections formed through entertainment media.
2020 – Javier Pérez de Cuéllar Dies
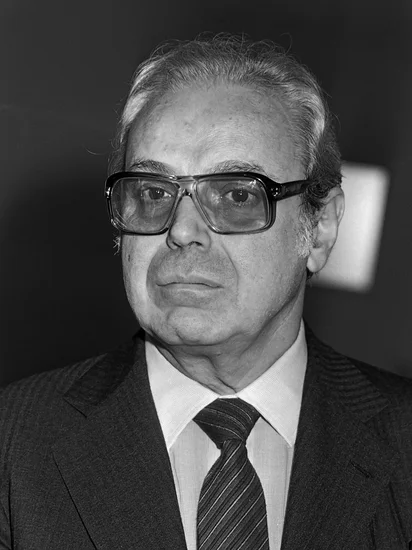

Peruvian diplomat and former United Nations Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar died, concluding a distinguished career in international relations. His diplomatic service spanned crucial decades of global change.
Pérez de Cuéllar’s UN leadership during the Cold War’s final years helped navigate numerous international crises. His commitment to multilateralism and peaceful conflict resolution earned worldwide respect.
Holidays and Observances on March 4
St. Casimir’s Day
Poland and Lithuania commemorate St. Casimir’s Day, honoring the patron saint of both nations. This religious observance celebrates the 15th-century prince known for his piety and dedication to justice.
St. Casimir’s legacy represents the shared Catholic heritage connecting Polish and Lithuanian cultures. The observance strengthens cultural bonds between these neighboring nations.
World Obesity Day
The global community observes World Obesity Day to raise awareness about obesity’s health impacts and promote prevention strategies. This international observance addresses one of the most pressing public health challenges.
The day encourages education about healthy lifestyle choices and policy changes to combat obesity. Healthcare professionals and advocates use this opportunity to promote wellness initiatives worldwide.
Christian Feast Days
The Christian calendar commemorates multiple saints on March 4, including Adrian of Nicomedia, Casimir, and Peter of Pappacarbone. These observances reflect the rich tradition of Christian martyrdom and devotion.
Each saint’s story contributes to the broader narrative of Christian faith and sacrifice. Their commemoration provides opportunities for reflection on spiritual values and religious commitment.
